Understanding Hydraulic Excavator Components
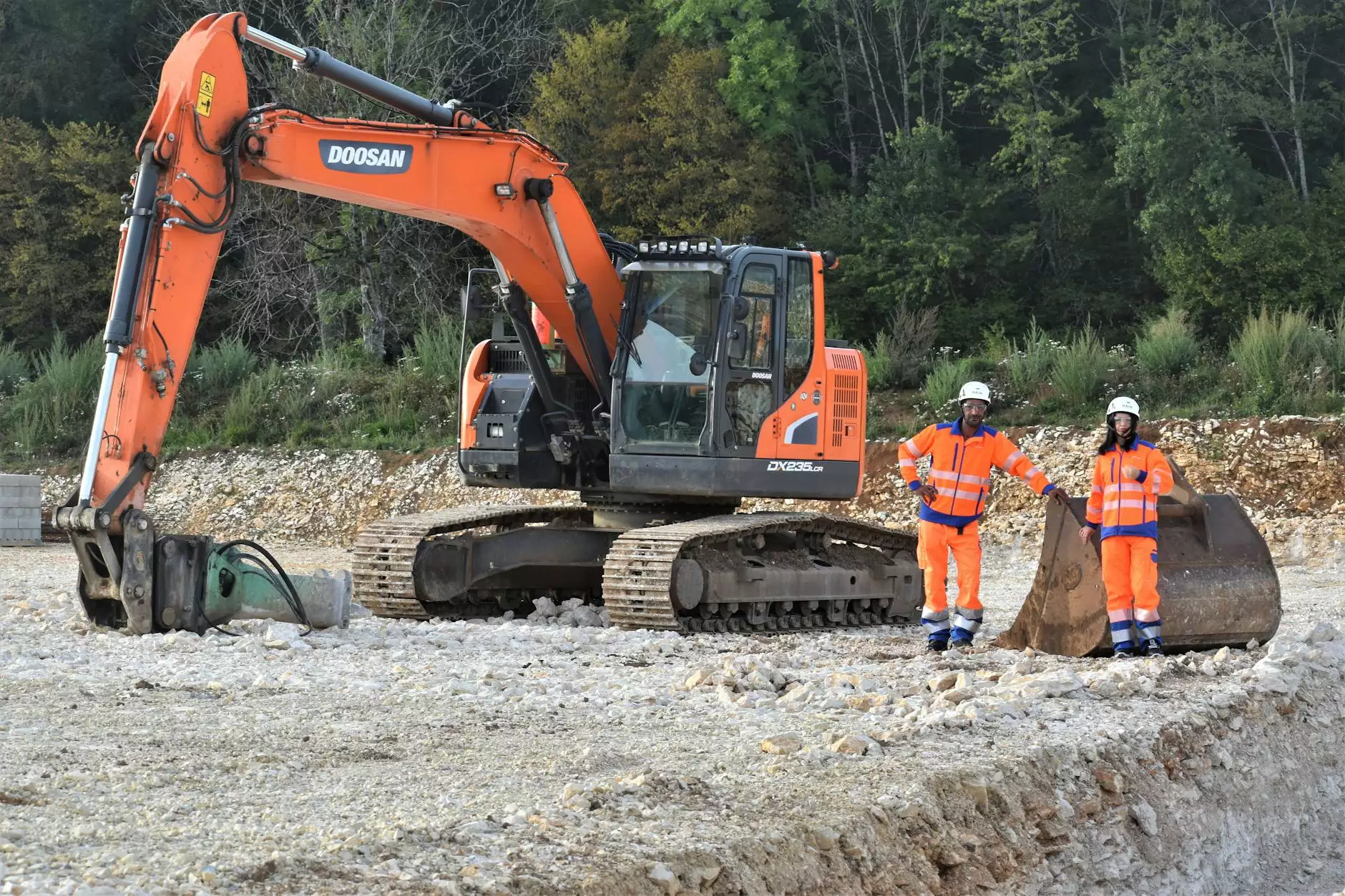

The world of construction and heavy machinery is vast and complex, with the hydraulic excavator standing out as one of the most versatile machines in the industry. Hydraulic excavators are essential in various applications, from digging foundations to demolishing structures. Their effectiveness stems largely from their numerous components, each playing a crucial role in the machinery's overall functionality. In this article, we will explore the intricate details of hydraulic excavator components, their functions, and why understanding them is vital for any professional or enthusiast in the field.
The Anatomy of Hydraulic Excavators
To appreciate the functionality of hydraulic excavators, it is essential to understand their core components. A hydraulic excavator primarily consists of the following parts:
- Crawler Tracks
- Boom
- Arm
- Bucket
- Hydraulic System
- Cab
- Counterweight
Crawler Tracks
The crawler tracks are vital for the mobility of hydraulic excavators. Unlike wheeled machines, crawler tracks provide greater stability and traction, especially on uneven or soft surfaces. They evenly distribute the weight of the excavator, reducing the risk of sinking into the ground. The design of these tracks allows the excavator to maneuver through various terrains, making it ideal for construction, mining, and landscaping projects.
Boom
The next significant component is the boom, which is the primary arm of the excavator extending upwards. The boom is engineered to lift heavy loads and facilitate digging operations. Typically constructed from high-strength steel, it is crucial that the boom maintains structural integrity under load. The boom's hydraulic cylinders enable it to pivot and reach various angles, making it an essential feature for precise digging and lifting.
Arm
Connected to the boom is the arm, also called the dipper or stick. The arm extends the reach of the excavator and is primarily responsible for positioning the bucket for excavation tasks. The hydraulic cylinders controlling the arm allow for exceptional precision, enabling operators to dig effectively even in confined spaces. The arm can also be fitted with various attachments, enhancing the excavator's versatility.
Bucket
At the end of the arm is the bucket—the implement tasked with actual excavation. Buckets come in various sizes and types, tailored for specific tasks such as digging, grading, or scooping. The design could vary from a standard bucket to specialized buckets like trenching or rock buckets, reflecting different operational needs.
Hydraulic System
The heart of any hydraulic excavator is its hydraulic system. This system uses hydraulic fluid to transmit power from the engine to the various components of the excavator, allowing them to move and function. The hydraulic system consists of hydraulic pumps, valves, and cylinders. Understanding this system is critical for operators, as proper maintenance is crucial for optimal performance. Regular checks on the hydraulic fluid levels and conditions can prevent costly breakdowns and extend the life of the machine.
Cab
The operator's cab is designed for comfort and functionality. It houses the controls for the excavator and provides visibility to the worksite. Modern excavators come equipped with advanced technology, including screens displaying real-time diagnostics, GPS tracking, and cameras for enhanced visibility. A well-designed cab can significantly improve efficiency, allowing operators to perform their tasks with greater ease and confidence.
Counterweight
The counterweight is often overlooked, but it plays a critical role in maintaining balance. By counteracting the weight of the boom and attachments, the counterweight prevents the excavator from tipping over during operations. The design and placement of the counterweight vary depending on the excavator's size and intended use, ensuring optimal stability and safety during excavation activities.
Importance of Regular Maintenance
Understanding the components of hydraulic excavators is not enough without recognizing the importance of regular maintenance. Routine checks can identify potential issues before they escalate into costly repairs.
Key Maintenance Tips
- Inspect Hydraulic Hoses: Regularly check for wear and leaks to prevent hydraulic failure.
- Monitor Fluid Levels: Ensure that hydraulic fluids are at optimal levels for smooth operation.
- Check Tracks and Undercarriage: Inspect the tracks for signs of wear and repair them immediately to maintain mobility.
- Clean Air Filters: Dirty filters can lead to reduced engine performance; regular cleaning ensures efficient operation.
- Assess Wiring and Electrical Systems: Ensure all electrical components are functioning properly to avoid unexpected failures.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the various hydraulic excavator components work in harmony to provide unmatched power and precision. Understanding each part's function not only enhances operational efficiency but also ensures safety on the job site. For those involved in the construction and heavy machinery industry, maintaining a solid comprehension of these components is essential for maximizing performance and minimizing downtime.
At Shop Hydraulic America, we offer a wide range of auto parts and supplies designed to support the maintenance and operation of hydraulic machines, including excavators. Our expert team is committed to providing quality components and exceptional customer service, ensuring that your machinery operates at its best.