Lung Cancer
Understanding Lung Cancer
Lung cancer is one of the most prevalent types of cancer, affecting millions of people worldwide. It occurs when abnormal cells in the lungs grow uncontrollably, forming tumors that can interfere with normal lung function.
Types of Lung Cancer
There are two main types of lung cancer:
1. Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC)
NSCLC is the most common type of lung cancer, accounting for approximately 85% of cases. It can be further categorized into:
- Adenocarcinoma: This type of NSCLC typically begins in the outer regions of the lungs and is commonly observed in non-smokers.
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Squamous cell carcinoma usually develops in the central airways of the lungs and is strongly associated with smoking.
- Large Cell Carcinoma: Large cell carcinoma accounts for a small percentage of NSCLC cases and often grows and spreads rapidly.
2. Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC)
SCLC is less common than NSCLC but tends to grow and spread more quickly. It is strongly linked to smoking and is often diagnosed in the advanced stages. SCLC is typically treated differently from NSCLC due to its aggressive nature.
Causes and Risk Factors
Smoking is the primary cause of lung cancer, with approximately 80% of cases attributed to tobacco use. However, non-smokers can also develop lung cancer, which suggests the involvement of other risk factors such as:
- Exposure to secondhand smoke
- Exposure to environmental pollutants like radon, asbestos, diesel exhaust, or certain chemicals
- Family history of lung cancer or genetic predisposition
- Previous radiation therapy to the chest
- Personal history of lung diseases like chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
Signs and Symptoms
The signs and symptoms of lung cancer may vary depending on the stage and type of cancer. Common symptoms include:
- Persistent cough or changes in coughing pattern
- Shortness of breath or wheezing
- Chest pain that worsens with deep breathing, coughing, or laughing
- Coughing up blood or rust-colored sputum
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue and weakness
- Hoarseness
- Repeated respiratory infections
- Swelling in the neck or face
Diagnosis and Treatment
Early detection plays a crucial role in successfully treating lung cancer. If you experience any signs or symptoms, it is important to consult a healthcare professional promptly. They may recommend the following diagnostic tests:
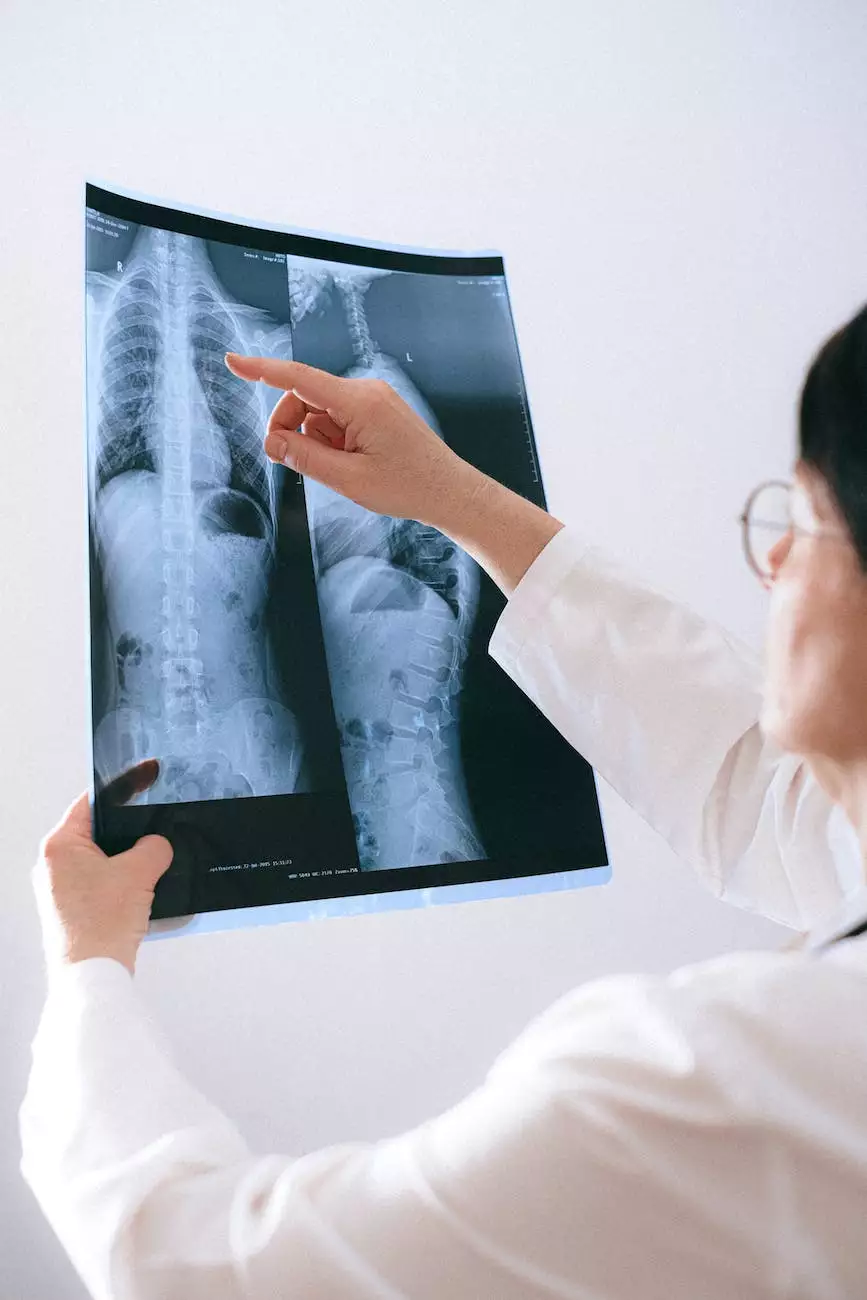
- Chest X-ray: This imaging test helps detect abnormalities in the lungs.
- CT Scan: A computed tomography (CT) scan provides more detailed images to determine the size, location, and spread of the tumor.
- Biopsy: A tissue sample is obtained from the lung for examination under a microscope to confirm the presence and type of cancer cells.
The treatment approach for lung cancer depends on various factors, including the stage, type, and overall health of the patient. It may involve:
- Surgery: The removal of the tumor and nearby lymph nodes may be recommended in the early stages of lung cancer.
- Radiation Therapy: High-energy radiation is used to kill cancer cells or shrink tumors.
- Chemotherapy: Drugs are administered to destroy cancer cells throughout the body.
- Targeted Therapy: Medications specifically target genetic changes in cancer cells to inhibit their growth.
- Immunotherapy: This treatment activates the body's immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells.
Resources and Support for Lung Cancer
At Sibel Blau, we understand the challenges faced by individuals affected by lung cancer. That's why we offer comprehensive resources and support in the health category. Our dedicated team provides up-to-date information, guidance, and emotional support to patients, their families, and caregivers.
By providing a multidisciplinary approach, we strive to ensure that everyone affected by lung cancer receives the highest standard of care, from diagnosis through treatment and survivorship.




